Product Description
-
Products: Free forging/Die forging products Material: Vacuum Degassed Ingot of Carbon Steel & Alloy steel & Stainless Steel and etc.; 13, 4130, 4140, 4150, 4340, 1035, 1045, EN9, EN19, EN24, EN31, 51200, SUJ2, 100Cr6, K310, 34CrNiMo6, 36CrNiMo4, 42CrMo4, 86CrMoV7, C35E, C40E, C45E, etc. Forging Equipments: 1.8tons, 6tons Electrical Hydraulic Hammer; 2.5ton, 1ton, 750KGS, 560KGS, 200KGS air hammers Heat treatment: Normalized/quench and temper/annealed/solution treatment/induction harden and etc. Machining Equipment: 1. Horizontal Turning Machine 2. Vertical Turning Machine 3. Milling Machine 4. Drilling Machie 5. CNC etc. Quality System: ISO9001: 2008 Cetificate: PED 97/23/EC, ABS, BV, GL, DNV Products Type: Maximum Diameter(mm) Max. length(mm) Maximum weight(ton) Ring 1500 400 10 Shaft 400 4000 10 Block 3500 / 8 Hollows 1500 3000 8 Flange 4900 400 8 Round bar 2000 8000 15 Unusual shapes 1500 400 8 Forging Ratio: ≥ 3.5 Annual Production Ability: 30000 tons Ultrasonic Test: Sep 1921-84 – Test Group 3 Class D or ASTM A388 – FBH max 4mm, customized QA & DOC: EN15718 3.1 Certificate, Chemical Composition Report, Mechanical Properties Report, UT Report (according to EN15718-3, SA388, Sep 1921 etc. ) Heat Treatment Report, Dimensions Check Report
- Required documents for offer to be provided by customer:
Drawings with formats of IGS (3D), DWG or DXF (Auto CAD 2D), PDF, JPG and
Standard of material (Preferable to provide Element Percentage of C, Si, Mn, P, S, etc and Physical/Machanical Properties of the material)
Technical requirements
Unit Weight of Rough
- Duration of pattern-making and sample-making: Within 30 days (Vary subject to the complexity of products)
- Minimum order: No limit
- Delivery: Within 30 working days after signing of contract and confirmation of samples by client
- Technological process:
- Workshop:
- Some Products:
- Testing equipments:
- Shipments:
- Company information:
- Certifications:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Forged Shaft |
|---|---|
| Application: | Mining Machinery |
| Certification: | ISO9001: 2000 |
| Condition: | New |
| Material: | Steel Alloy, Customer′s Requirement |
| Transport Package: | Carton and Wooden Box, Customer′s Request |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the key differences between live axles and dead axles in vehicle design?
In vehicle design, live axles and dead axles are two different types of axle configurations with distinct characteristics and functions. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key differences between live axles and dead axles:
Live Axles:
A live axle, also known as a solid axle or beam axle, is a type of axle where the wheels on both ends of the axle are connected and rotate together as a single unit. Here are the key features and characteristics of live axles:
- Connected Wheel Movement: In a live axle configuration, the wheels on both ends of the axle are linked together, meaning that any movement or forces applied to one wheel will directly affect the other wheel. This connection provides equal power distribution and torque to both wheels, making it suitable for off-road and heavy-duty applications where maximum traction is required.
- Simple Design: Live axles have a relatively simple design, consisting of a solid beam that connects the wheels. This simplicity makes them durable and capable of withstanding heavy loads and rough terrains.
- Weight and Cost: Live axles tend to be heavier and bulkier compared to other axle configurations, which can impact the overall weight and fuel efficiency of the vehicle. Additionally, the manufacturing and maintenance costs of live axles can be lower due to their simpler design.
- Suspension: In most cases, live axles are used in conjunction with leaf spring or coil spring suspensions. The axle is typically mounted to the vehicle’s chassis using leaf springs or control arms, allowing the axle to move vertically to absorb bumps and provide a smoother ride.
- Off-road Capability: Live axles are commonly used in off-road vehicles, trucks, and heavy-duty applications due to their robustness, durability, and ability to deliver power to both wheels simultaneously, enhancing traction and off-road performance.
Dead Axles:
A dead axle, also known as a dummy axle or non-driven axle, is a type of axle that does not transmit power to the wheels. It is primarily used to provide support and stability to the vehicle. Here are the key features and characteristics of dead axles:
- Independent Wheel Movement: In a dead axle configuration, each wheel operates independently, meaning that the movement or forces applied to one wheel will not affect the other wheel. Each wheel is responsible for its own power delivery and traction.
- Weight Distribution: Dead axles are often used to distribute the weight of the vehicle more evenly, especially in cases where heavy loads need to be carried. By adding an extra axle without driving capability, the weight can be distributed over a larger area, reducing the load on other axles and improving stability.
- Steering: Dead axles are commonly used as front axles in vehicles with rear-wheel drive configurations. They provide support for the front wheels and allow for steering control. The steering is typically achieved through a separate mechanism, such as a steering linkage or a steering gear.
- Reduced Complexity: Dead axles are simpler in design compared to live axles since they do not have the additional components required for power transmission. This simplicity can lead to lower manufacturing and maintenance costs.
- Efficiency and Maneuverability: Dead axles are often used in vehicles where power delivery to all wheels is not necessary, such as trailers, certain types of buses, and some light-duty vehicles. By eliminating the power transmission components, these vehicles can achieve better fuel efficiency and improved maneuverability.
It’s important to note that the choice between live axles and dead axles depends on the specific application, vehicle type, and desired performance characteristics. Vehicle manufacturers consider factors such as load capacity, traction requirements, off-road capability, cost, and fuel efficiency when determining the appropriate axle configuration for a particular vehicle model.

How do axle ratios impact the performance and fuel efficiency of a vehicle?
The axle ratio of a vehicle plays a crucial role in determining its performance characteristics and fuel efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation of how axle ratios impact these aspects:
Performance:
The axle ratio refers to the ratio of the number of rotations the driveshaft makes to the number of rotations the axle makes. A lower axle ratio, such as 3.23:1, means the driveshaft rotates 3.23 times for every rotation of the axle, while a higher ratio, like 4.10:1, indicates more driveshaft rotations per axle rotation.
A lower axle ratio, also known as a numerically higher ratio, provides better low-end torque and acceleration. This is because the engine’s power is multiplied as it goes through the gears, resulting in quicker acceleration from a standstill or at lower speeds. Vehicles with lower axle ratios are commonly found in trucks and performance-oriented vehicles where quick acceleration and towing capacity are desired.
On the other hand, a higher axle ratio, or numerically lower ratio, sacrifices some of the low-end torque for higher top-end speed and fuel efficiency. Vehicles with higher axle ratios are typically used in highway driving scenarios where maintaining higher speeds and maximizing fuel efficiency are prioritized.
Fuel Efficiency:
The axle ratio directly affects the engine’s RPM (revolutions per minute) at a given vehicle speed. A lower axle ratio keeps the engine running at higher RPMs, which may result in increased fuel consumption. However, this ratio can provide better towing capabilities and improved off-the-line acceleration.
In contrast, a higher axle ratio allows the engine to operate at lower RPMs during cruising speeds. This can lead to improved fuel efficiency because the engine doesn’t have to work as hard to maintain the desired speed. It’s worth noting that other factors, such as engine efficiency, aerodynamics, and vehicle weight, also influence fuel efficiency.
Manufacturers carefully select the axle ratio based on the vehicle’s intended purpose and desired performance characteristics. Some vehicles may offer multiple axle ratio options to cater to different driving preferences and requirements.
It’s important to consider that changing the axle ratio can have implications on the overall drivetrain system. Modifying the axle ratio can affect the vehicle’s speedometer accuracy, transmission shifting points, and may require recalibration of the engine control unit (ECU) to maintain optimal performance.
As always, for precise information on a specific vehicle’s axle ratio and its impact on performance and fuel efficiency, it is best to consult the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications or consult with automotive experts.
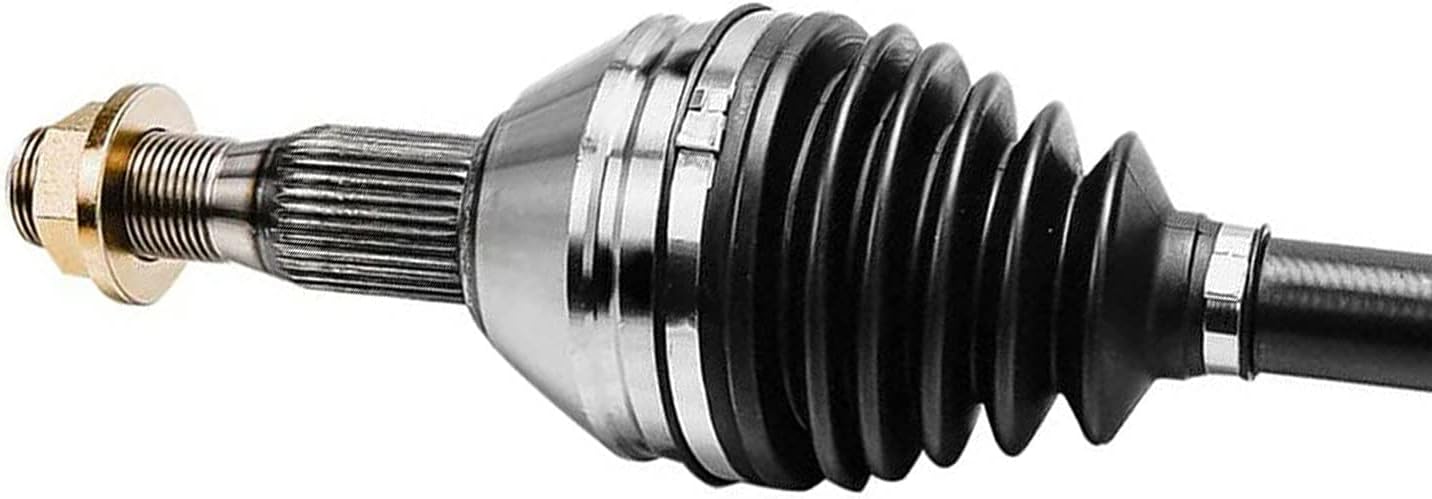

What is the primary function of an axle in a vehicle or machinery?
An axle plays a vital role in both vehicles and machinery, providing essential functions for their operation. The primary function of an axle is to transmit rotational motion and torque from an engine or power source to the wheels or other rotating components. Here are the key functions of an axle:
- Power Transmission:
- Support and Load Bearing:
- Wheel and Component Alignment:
- Suspension and Absorption of Shocks:
- Steering Control:
- Braking:
An axle serves as a mechanical link between the engine or power source and the wheels or driven components. It transfers rotational motion and torque generated by the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle or machinery to move. As the engine rotates the axle, the rotational force is transmitted to the wheels, propelling the vehicle forward or driving the machinery’s various components.
An axle provides structural support and load-bearing capability, especially in vehicles. It bears the weight of the vehicle or machinery and distributes it evenly across the wheels or supporting components. This load-bearing function ensures stability, balance, and proper weight distribution, contributing to safe and efficient operation.
The axle helps maintain proper alignment of the wheels or rotating components. It ensures that the wheels are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the ground, promoting stability and optimal tire contact with the road surface. In machinery, the axle aligns and supports the rotating components, ensuring their correct positioning and enabling smooth and efficient operation.
In vehicles, particularly those with independent suspension systems, the axle plays a role in the suspension system’s operation. It may incorporate features such as differential gears, CV joints, or other mechanisms that allow the wheels to move independently while maintaining power transfer. The axle also contributes to absorbing shocks and vibrations caused by road irregularities, enhancing ride comfort and vehicle handling.
In some vehicles, such as trucks or buses, the front axle also serves as a steering axle. It connects to the steering mechanism, allowing the driver to control the direction of the vehicle. By turning the axle, the driver can steer the wheels, enabling precise maneuverability and navigation.
An axle often integrates braking components, such as brake discs, calipers, or drums. These braking mechanisms are actuated when the driver applies the brakes, creating friction against the rotating axle or wheels and causing deceleration or stopping of the vehicle. The axle’s design can affect braking performance, ensuring effective and reliable stopping power.
Overall, the primary function of an axle in both vehicles and machinery is to transmit rotational motion, torque, and power from the engine or power source to the wheels or rotating components. Additionally, it provides support, load-bearing capability, alignment, suspension, steering control, and braking functions, depending on the specific application and design requirements.


editor by CX 2024-03-27
China manufacturer 2.5 Ton Underground Mining Battery Locomotive Machine Machinery Equipment Electric Battery Mining Locomotive near me supplier
Product Description
Product Description
2.5 Ton Underground Mining Battery Locomotive, Electric Battery Mining Locomotive
HangZhou CZPT battery electric locomotive is a kind of track traction equipment powered by batteries, which is generally used in mines. There are 2 types of battery electric locomotives, explosion-proof type and ordinary type. The explosion-proof type is mainly used in coal mines. There are also many options in terms of speed regulation and braking methods. Speed control methods include resistance speed control, chopping speed control and frequency conversion speed control. Braking methods include pure mechanical braking, hydraulic braking and compressed air braking. In addition, electric braking can also be selected as an auxiliary braking method.
| Adhesive / total weight (t) | 2.5 | |
| Track gauge (mm) | 600,762 or 900 | |
| Traction (KN) | 2.55 | |
| Max. Traction (KN) | 6.13 | |
| Speed(km/h) | 4.54 | |
| Battery Voltage (V) | 48 | |
| Battery Capacity (Ah) | 330 | |
| Power (KW) | 3.5*1 | |
| Dimensions Length(mm) | 2360 | |
| Width(mm) | 914,1076 or 1214 | |
| Height(mm) | 1550 | |
| Wheelbase (mm) | 650 | |
| Wheel diameter (mm) | 460 | |
| Min Curve radius (m) | 5 | |
| Controller | Resistance or IGBT | |
| Braking method | Mechanical Brake |
Locomotive Spareparts
Detailed Photos
Advantages of our product
1.Using high-quality steel plates, special rust removal process make sure it more anti-corrosion and suitable for harsh mining environment.
2. Producing motors ourselves, using high lever insulation material and pure copper, ensure the powerful traction force, and suitable for harsh mining environment.
3.Gear anastomosis surface to reach more than 80%, which is far more exceeding the standard.
4.Professionally designed and adjusted frame ensure safe driving and avoids falling off rails.
5.A variety of braking methods can be choose, air brake, hydraulic brake, electric brake, mechanical brake to ensure the safety drive.
6. 40 years richful experience with the ability to design and make customized product according to your requirements.
7. Proving factory online-visiting
Product Factory Test
Mining Locomotive test
1.Before Running the locomotive,carry out gear debugging, lighting, gear, and brake adjustment etc.To ensure the normal operation of the locomotive.
2.Carry out a tensile test before leaving the factory to ensure the load performance of the locomotive meets the standard. Our design standards generally exceed the national standard by 10%-20%.
3.Carry out different type running test before leaving the factory to ensure the performance and normal operation of the whole locomotive. It can adapt to various harsh conditions under simulated working conditions.
Motor test
The motor has to go through many inspection procedures before leaving the factory, and each motor has to be carried out with load running experiments.
Explosion-proof motors are carried out with water pressure test.
All the test of motor is to ensure that can adapt to harsh working conditions.
Clients Feedback and Cases
1. A good feedback of our lithium battery locomotive from a client of Latin America
2. In order to solve the exist problems of lead-acid batteries. More than 30 lead-acid battery electric locomotives in this large mining were changed into lithium battery electric locomotives, which improved the work enthusiasm and production efficiency of employees, reduced costs,and more environment-friendly.
3. The mining rock drill car designed by Sunward Co., has a small size and simple structure, so the space for placing the lithium battery on the body is very limited.
According to the limitation size, our company design a lithium power supply power plan, which
perfectly solves the problem of lithium power supply space.
In order to adapt to the special industrial and mining environment and improve transportation efficiency, a batch of 2.5-ton lithium battery electric locomotives are designed to Myanmar Clients.
Company Profile
FAQ
What‘s your product advantages?
We have more 40 years experience in this field so that we could design or produce the locomotive as your requirement. We could also provide online service to teach you how to operate and maintain the locomotive.
The most important thing that we produce the main part of the locomotive- The traction motors. we could guarante the power of the locomotive.
Pre-sales Service:
The wide product range enables us to provide our customers with individual machines or complete processing plants. Based on our customer’s request and budget, our experts make efficient and reliable solutions, and we produce strictly follow customers’ order. What’s more, every customer has the chance to visit the working machine in the site before placing the order.
After-sales Service:
Experienced technicians guidance is available on the phone, and on the internet. One or more engineers will be dispatched to the quarry site to help install the customer’s plants.Necessary training about machine daily maintenance to local workers is provided also.
Methods of Payment:
T/T (Telegraphic Transfer) or Western Union or L/C at sight
Handling time for an order:
Within 10 days supplied from stock
Shipping method:
Sample order: we suggest Courier express like DHL/UPS/TNT/FEDEX or by air
Bulk order: we suggest by air or by sea.
Quality Control:
We have our own experienced QC.
There will be strict inspection and testing for every order before shipping out.
After Services:
a. Our sales team will response for your question within 24 hours (Holiday is Excluded)
b. Technical Support will be available in any time
c. Free replacement will provide once the failure confirmed caused by our product quality
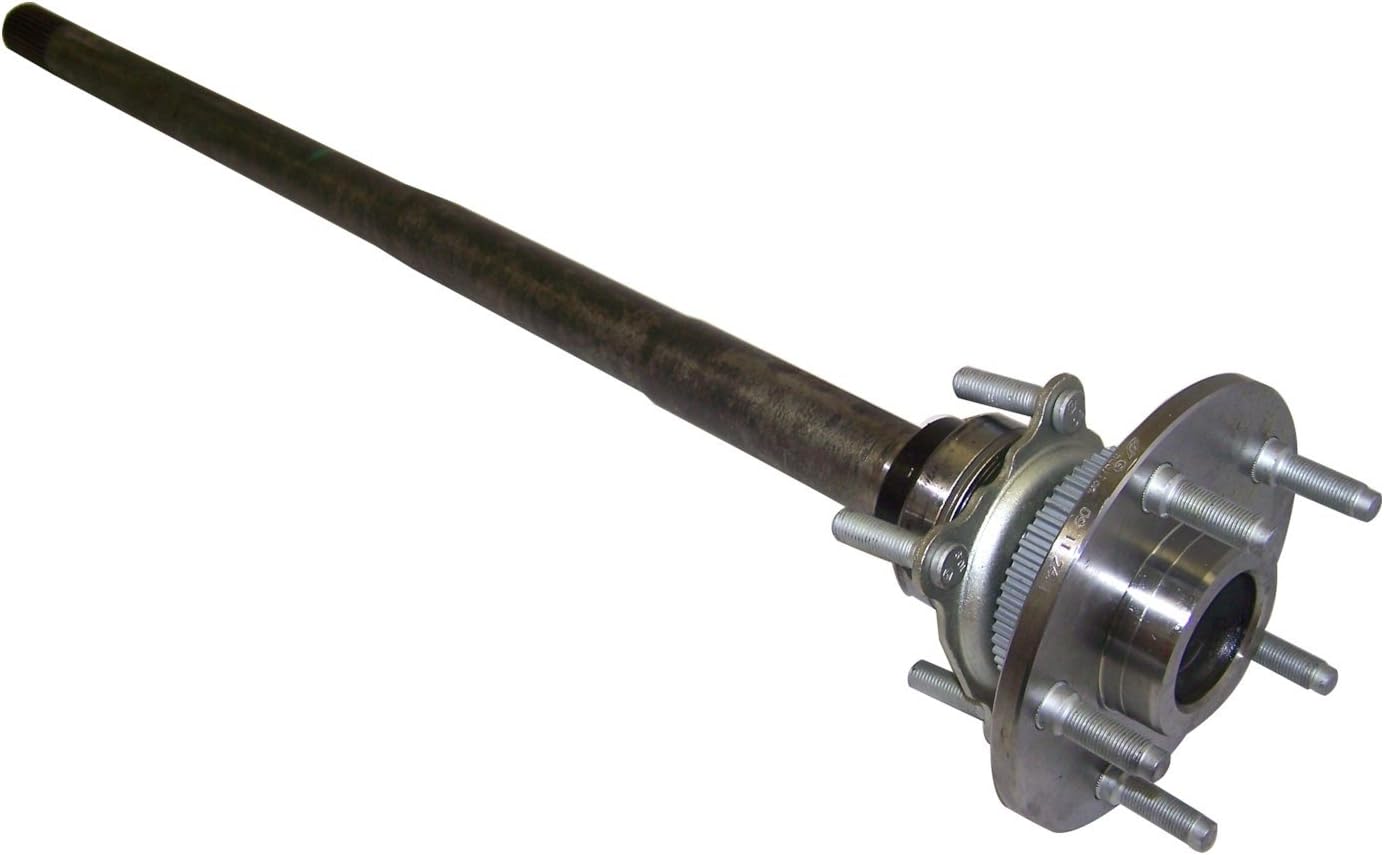
The 5 components of an axle, their function and installation
If you’re considering replacing an axle in your vehicle, you should first understand what it is. It is the component that transmits electricity from 1 part to another. Unlike a fixed steering wheel, the axles are movable. The following article will discuss the 5 components of the half shaft, their function and installation. Hopefully you were able to identify the correct axle for your vehicle. Here are some common problems you may encounter along the way.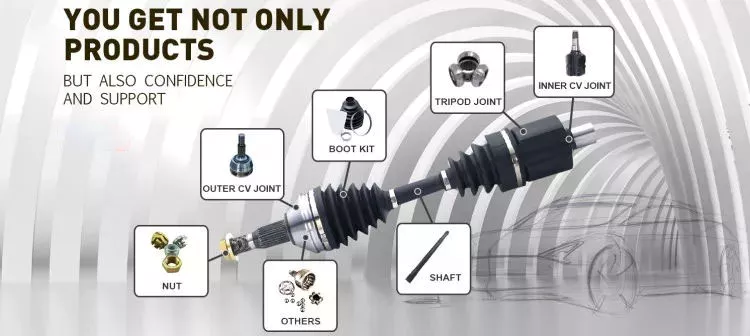
five components
The 5 components of the shaft are flange, bearing surface, spline teeth, spline pitch and pressure angle. The higher the number of splines, the stronger the shaft. The maximum stress that the shaft can withstand increases with the number of spline teeth and spline pitch. The diameter of the shaft times the cube of the pressure angle and spline pitch determines the maximum stress the shaft can withstand. For extreme load applications, use axles made from SAE 4340 and SAE 1550 materials. In addition to these 2 criteria, spline rolling produces a finer grain structure in the material. Cutting the splines reduces the strength of the shaft by 30% and increases stress.
The asymmetric length of the shaft implies different torsional stiffness. A longer shaft, usually the driver’s side, can handle more twist angles before breaking. When the long axis is intact, the short axis usually fails, but this does not always happen. Some vehicles have short axles that permanently break, causing the same failure rate for both. It would be ideal if both shafts were the same length, they would share the same load.
In addition to the spline pitch, the diameter of the shaft spline is another important factor. The small diameter of a spline is the radius at which it resists twisting. Therefore, the splines must be able to absorb shock loads and shocks while returning to their original shape. To achieve these goals, the spline pitch should be 30 teeth or less, which is standard on Chrysler 8.75-inch and GM 12-bolt axles. However, a Ford 8.8-inch axle may have 28 or 31 tooth splines.
In addition to the CV joints, the axles also include CV joints, which are located on each end of the axle. ACV joints, also known as CV joints, use a special type of bearing called a pinion. This is a nut that meshes with the side gear to ensure proper shaft alignment. If you notice a discrepancy, take your car to a shop and have it repaired immediately.
Function
Axles play several important roles in a vehicle. It transfers power from the transmission to the rear differential gearbox and the wheels. The shaft is usually made of steel with cardan joints at both ends. Shaft Shafts can be stationary or rotating. They are all creatures that can transmit electricity and loads. Here are some of their functions. Read on to learn more about axles. Some of their most important features are listed below.
The rear axle supports the weight of the vehicle and is connected to the front axle through the axle. The rear axle is suspended from the body, frame and axle housing, usually spring loaded, to cushion the vehicle. The driveshaft, also called the propshaft, is located between the rear wheels and the differential. It transfers power from the differential to the drive wheels.
The shaft is made of mild steel or alloy steel. The latter is stronger, more corrosion-resistant and suitable for special environments. Forged for large diameter shafts. The cross section of the shaft is circular. While they don’t transmit torque, they do transmit bending moment. This allows the drive train to rotate. If you’re looking for new axles, it’s worth learning more about how they work.
The shaft consists of 3 distinct parts: the main shaft and the hub. The front axle assembly has a main shaft, while the rear axle is fully floating. Axles are usually made of chrome molybdenum steel. The alloy’s chromium content helps the axle maintain its tensile strength even under extreme conditions. These parts are welded into the axle housing.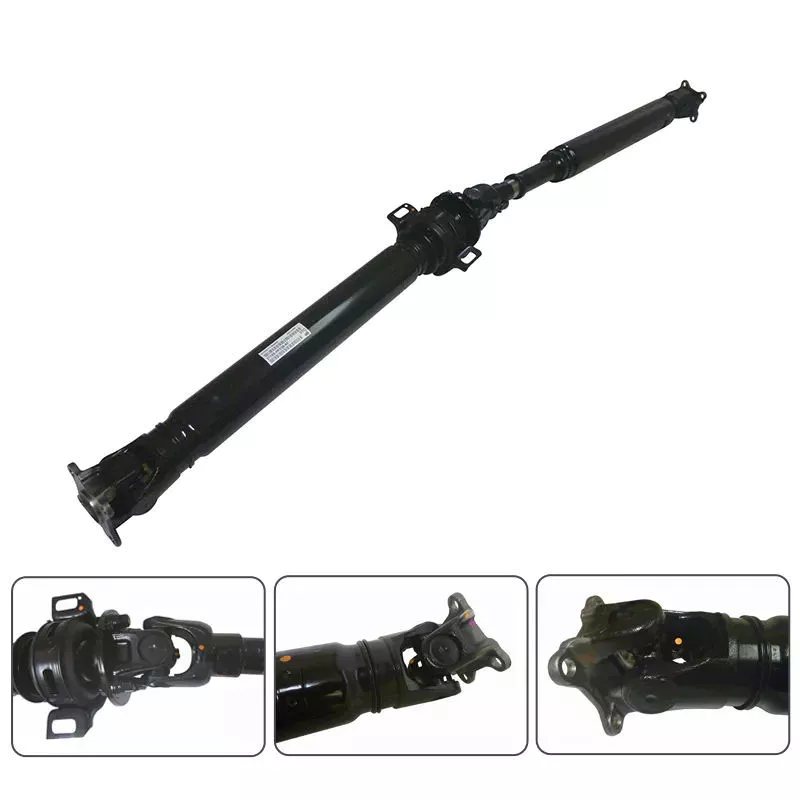
Material
The material used to make the axle depends on the purpose of the vehicle. For example, overload shafts are usually made of SAE 4340 or 1550 steel. These steels are high strength low alloy alloys that are resistant to bending and buckling. Chromium alloys, for example, are made from steel and have chromium and molybdenum added to increase their toughness and durability.
The major diameter of the shaft is measured at the tip of the spline teeth, while the minor diameter is measured at the bottom of the groove between the teeth. These 2 diameters must match, otherwise the half shaft will not work properly. It is important to understand that the brittleness of the material should not exceed what is required to withstand normal torque and twisting, otherwise it will become unstable. The material used to make the axles should be strong enough to carry the weight of a heavy truck, but must also be able to withstand torque while still being malleable.
Typically, the shaft is case hardened using an induction process. Heat is applied to the surface of the steel to form martensite and austenite. The shell-core interface transitions from compression to tension, and the peak stress level depends on the process variables used, including heating time, residence time, and hardenability of the steel. Some common materials used for axles are listed below. If you’re not sure which material is best for your axle, consider the following guide.
The axle is the main component of the axle and transmits the transmission motion to the wheels. In addition, they regulate the drive between the rear hub and the differential sun gear. The axle is supported by axle bearings and guided to the path the wheels need to follow. Therefore, they require proper materials, processing techniques and thorough inspection methods to ensure lasting performance. You can start by selecting the material for the shaft.
Choosing the right alloy for the axle is critical. You will want to find an alloy with a low carbon content so it can harden to the desired level. This is an important consideration because the hardenability of the alloy is important to the durability and fatigue life of the axle. By choosing the right alloy, you will be able to minimize these problems and improve the performance of your axle. If you have no other choice, you can always choose an alloy with a higher carbon content, but it will cost you more money.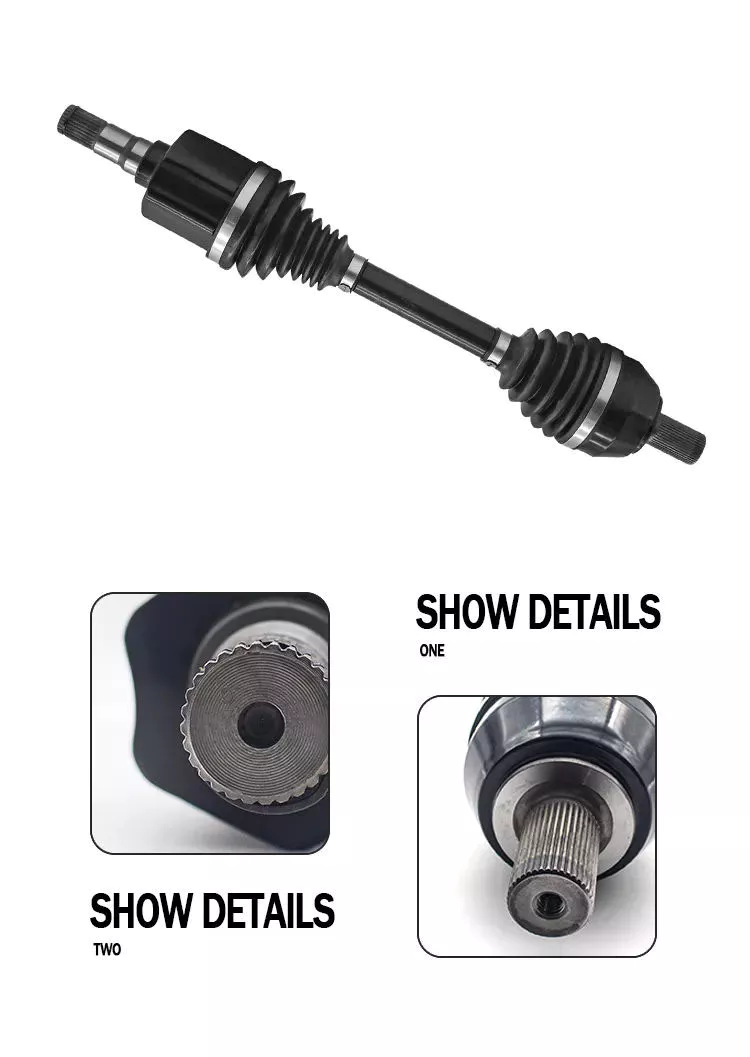
Install
The process of installing a new shaft is simple. Just loosen the axle nut and remove the set bolt. You may need to tap a few times to get a good seal. After installation, check the shaft at the points marked “A” and “D” to make sure it is in the correct position. Then, press the “F” points on the shaft flange until the points are within 0.002″ of the runout.
Before attempting to install the shaft, check the bearings to make sure they are aligned. Some bearings may have backlash. To determine the amount of differential clearance, use a screwdriver or clamp lever to check. Unless it’s caused by a loose differential case hub, there shouldn’t be any play in the axle bearings. You may need to replace the differential case if the axles are not mounted tightly. Thread adjusters are an option for adjusting drive gear runout. Make sure the dial indicator is mounted on the lead stud and loaded so that the plunger is at right angles to the drive gear.
To install the axle, lift the vehicle with a jack or crane. The safety bracket should be installed under the frame rails. If the vehicle is on a jack, the rear axle should be in the rebound position to ensure working clearance. Label the drive shaft assemblies and reinstall them in their original positions. Once everything is back in place, use a 2-jaw puller to pry the yoke and flange off the shaft.
If you’ve never installed a half shaft before, be sure to read these simple steps to get it right. First, check the bearing surfaces to make sure they are clean and undamaged. Replace them if they look battered or dented. Next, remove the seal attached to the bushing hole. Make sure the shaft is installed correctly and the bearing surfaces are level. After completing the installation process, you may need to replace the bearing seals.

